Pear Tarte Tatin

Ingredientes







Instrucciones
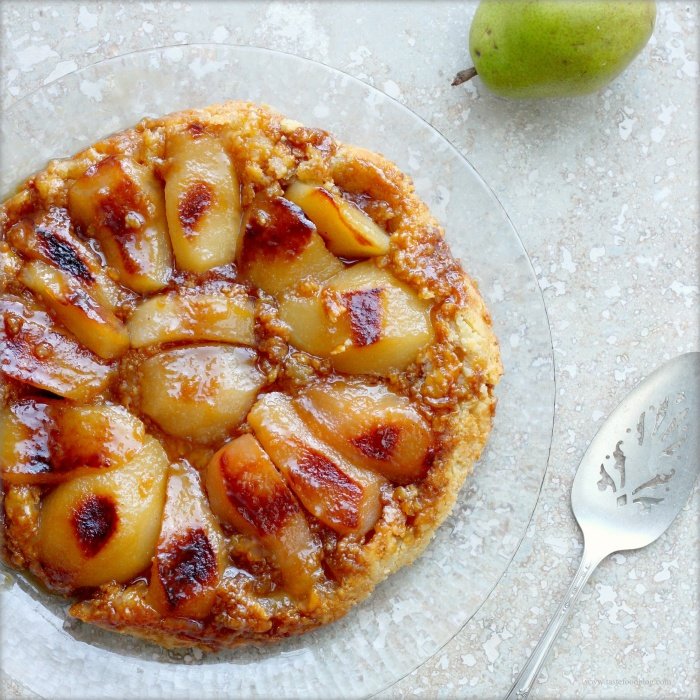
Core the pears, then peel as neatly as possible and halve. If you like, they can be prepared up to a day ahead and kept in the fridge, uncovered, so that they dry out.
Tip the sugar, butter, star anise, cardamom and cinnamon into an ovenproof frying pan, about 20cm wide, and place over a high heat until bubbling. Shake the pan and stir the buttery sauce until it separates and the sugar caramelises to a toffee colour.
Lay the pears in the pan, then cook in the sauce for 10-12 mins, tossing occasionally, until completely caramelised. Don’t worry about them burning – they won’t – but you want to caramelise them as much as possible. Splash in the brandy and let it flambé, then set the pears aside.
Heat oven to 200C/fan 180C/gas 6. Roll the pastry out to the thickness of a £1 coin. Using a plate slightly larger than the top of the pan, cut out a circle, then press the edges of the circle of pastry to thin them out.
When the pears have cooled slightly, arrange them in the pan, cut side up, in a floral shape, with the pears around the edge pointing inwards. Rest the cinnamon stick on the top in the centre, with the cardamom pods scattered around.
Drape the pastry over the pears, then tuck the edges down the pan sides and under the fruit (see Gordon’s guide). Pierce the pastry a few times, then bake for 15 mins. If a lot of juice bubbles up the side of the pan, pour it off at this stage (see guide). Reduce oven to 180C/fan 160C/gas 4 and bake for 15 mins more until the pastry is golden. Leave the tart to stand for 10 mins, then invert it carefully onto a serving dish.

 Calculadora de IMC
Calculadora de IMC Calculadora de Calorías
Calculadora de Calorías Calculadora de Porcentaje de Grasa Corporal
Calculadora de Porcentaje de Grasa Corporal Calculadora de TMB
Calculadora de TMB












